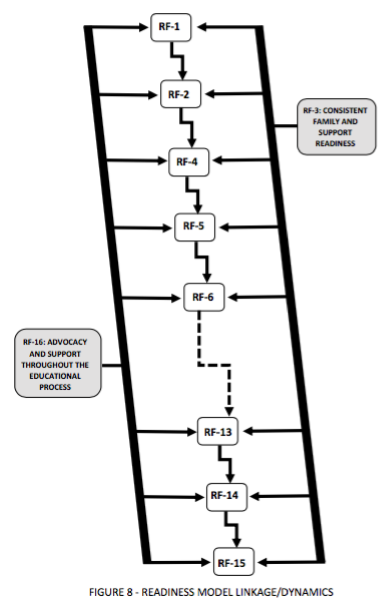
Figure 8: Readiness Model Linkage and Dynamics
DEFINITION: Referring to Figure 6 which focuses upon the overall educational process that yields both 'prepared' students amd 'unprepared' students; the 'prepared' students inevitably achieve a very acceptable quality of life whereas the 'unprepared' students inherit some of the poverty-inequalities and a quality of life that is unfair, undeserved, unnecessary and wholly unacceptable. Figure 7 also addresses the importance of 'preparation' and that learning is dependent upon the readiness to learn and that 'preparation' is very much dependent upon readiness [to learn] and learning, per se, i.e., Readiness [to learn] + Learning = Preparation [to move on to the next step]. Figure 8 depicts the readiness model linkage and dynamics.
Description: Two observations of Figure 8 follow: [1] RF-3 and RF-16 are in parallel with RF-1, RF-2, RF-4, RF-5,..., RF-15. i.e., these two readiness factors are continuous functions throughout the educational process and differ in accordance with the growing spectrum of different student populatios. [2] In parallel with RF-3 and RF-16 is a serial sequence of readiness factors and like the proverbial 'chain' that is only as strong as its weakest link. Herein lies the predicament: As a student experiences the educational process with 'acceptable readiness factors' - as exist in most schoolsettings beyond the poverty arena - the outcomes are certainly 'acceptable' or 'better than acceptable'. Conversely, if one of the readiness factors, i.e., RF-1, Rf-2,..., RF-16, are not acceptable, then the outcomes are compromised to some extent. However, if more than one readiness factor is not acceptable, then the compromose to outcomes is further compromised. In areas of continuing poverty, the readiness factors that come into play include most, if not all, of the readiness factors. The resultant compromise to outcomes is devastating! Either one of two outcomes are [1] students advance from one grade to the next 'unprepared' remember social promotions?]; there is an imbedded ripple factor in this arrangement, i.e., the student becomes more and 'unprepared' for educational success. [2] the student is suspended, expelled or simply stops attending school. Either outcome is a disservice to the student and to society.
Keywords: Learning eadiness, teaching readiness, educational preparation, educational advocacy/support/interventions, life readiness, learning readiness for life skills, expelled students, disciplined students, problem students, drop-outs, chronic ansenteeism, children who don't enter school, employment readiness, upward mobility readiness, readiness metrics, readiness assessment.
Selected References :
1. Primary School Readiness Assessment, posted in EDUCATION, Nadine, August, 2008.
2. 3 Middle Grade Indicators of Reainess, Executive Summary, November, 2014.
3. Middle Grades and the Transition to High School, University of Chicago, Consortium on Chicago School Readiness, The University of Chicago, 2015.
4. Metrics for 'High School Readiness', Applied Survey Research, 2007.
5. College readiness: Education Week Webinar, Carole Adams, Contibuting Writer, Education Week, College readiness and Life Skills: Moving Beyond Academics, January 31, 2013.
6. Redefining College Readiness, David T. Conley,,,,, Prepared for the Bill & Melissa Gates Foundation, March, 2007.
7. What Is Employment Readiness/, Employment Readiness Model, Valerie G. Ward Consultants Ltd., 2015.